The primary classification tool within MQC is the class map. Each class map contains one or more match statements, which specify criteria that must be met for traffic identification
Because classmaps can contain multiple match statements, when a class map is defined, a logical operator for the discrete match statements also needs to be defined. Two options exist as follows:
- match-all (a logical AND operator), meaning that all match statements must be true at the same time for the class map condition to be true; match-all is the default operator; it is important not to use mutually exclusive match criteria when a match-all operator is defined within the class map, as this combination can never yield a positive match.
- match-any (a logical OR operator), meaning that any of the match statements might be true for the class map condition to be true.
These match statements specify the criteria for traffic identification. These can include the following:
- Layer 1 parameters: Physical interface, subinterface, PVC, or port
- Layer 3 parameters: Differentiated Services Code Points (DSCP), source/destination IP address
- Layer 4 parameters: TCP or UDP ports
- Layer 7 parameters: Application signatures and URLs in packet headers or payload through Network Based Application Recognition (NBAR)
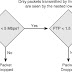
Figure 1 illustrates the Layer 2 to Layer 7 packet classification criteria; however, due to space limitations, the diagram is not to scale, nor are all fields indicated.










No comments:
Post a Comment