It is common to have one or more participants who cannot attend the meeting in person but are available to dial in and attend through a phone. These callers need to join the TelePresence meeting through an audio-only call, which known as the Audio Add-In feature.
In addition to AAC-LD, Cisco TelePresence also supports the G.711 audio encoding standard. This makes it interoperable with virtually any telephone device or audio conferencing bridge whether that is a standard Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) phone, a cellular phone, an IP Phone, or an audio-conferencing bridging service, such as Cisco Meetingplace, Cisco Webex, or the numerous other audio bridging services in the market.
The feature is invoked just like it is on regular telephones and cellular phones. The user simply presses the Conference softkey on the Cisco TelePresence IP Phone user interface and places a standard telephone call to the destination phone number. Alternatively, the remote person can dial the telephone number of the TelePresence room, and the user can answer the incoming call and then press the Conference/Join softkey to bridge the caller in.
Under the hood, the way this feature works is that the audio call is established as a completely separate session. (It is signaled using the Session Initiation Protocol [SIP], and a G.711 RTP stream is negotiated.) The RTP stream of audio coming into the TelePresence system from the remote party is decoded and blended out all of the speakers (just like the auxiliary audio is) and is simultaneously mixed in with the auxiliary audio stream going out to all the other participating TelePresence rooms, allowing all the TelePresence participants to hear the audio caller. In the opposite direction, sound coming from all three microphones within the room, with all three of the audio channels received from the other participating TelePresence rooms, is mixed and sent out over the G.711 RTP stream to the audio participant, allowing him to hear everything that’s said by the TelePresence participants. Figure 1 illustrates how this is done.
| Note | Future versions of Cisco TelePresence might incorporate support for additional audio algorithms for the audio add-in stream, such as G.722, to increase the fidelity of the Audio Add-In participant. |
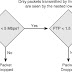
If multiple audio-only participants are needed, the user can use an audio conferencing bridging service, such as Cisco Webex, as illustrated in Figure 2.
To successfully dial into a bridging service such as Cisco Webex, the TelePresence user initiating the Audio Add-In feature must navigate the Interactive Voice Response (IVR) menu of the bridging service and enter the correct conferencing ID number and password to join that audio meeting. This is a good segue into the next topic, DTMF.











No comments:
Post a Comment