The intercompany deployment model connects not only TelePresence systems within an enterprise, but also allows for TelePresence systems within one enterprise to call systems within another enterprise. The intercompany model expands on the intracampus and intra-enterprise models to include connectivity between different enterprises, both in a point-to-point or in a multipoint manner. It offers a significant increase in value to the TelePresence deployment by greatly increasing the number of endpoints to which a unit can communicate. This model is also at times referred to as the business-to-business (B2B) TelePresence deployment model.
The intercompany model offers the most flexibility and is suitable for businesses that often require employees to travel extensively for both internal and external meetings. In addition to the business advantages of the intra-enterprise model, the intercompany deployment model lets employees maintain high-quality customer relations without the associated costs of travel time and expense.
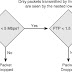
The network infrastructure of the intercompany deployment model builds on the intra-enterprise model and requires the enterprises to share a common MPLS VPN service provider. Additionally, the MPLS VPN service provider must have a “shared services” Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instance provisioned with a Cisco IOS XR Session/Border Controller (SBC).
The Cisco SBC bridges a connection between two separate MPLS VPNs to perform secure inter-VPN communication between enterprises. Additionally, the SBC provides topology and address hiding services, NAT and firewall traversal, fraud and theft of service prevention, DDoS detection and prevention, call admission control policy enforcement, encrypted media pass-through, and guaranteed QoS.
Although the focus of this chapter is TelePresence deployments within the enterprise, several of these options can be hosted or managed by service providers. For example, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Cisco TelePresence Manager servers and multipoint resources can be located on-premise at one of the customer campus locations, colocated within the service provider network (managed by the enterprise), or hosted within the service provider network (managed by the service provider). However, with the exception of interVPN elements required by providers offering intercompany TelePresence services, the TelePresence solution components and network designs remain fundamentally the same whether the TelePresence systems are hosted/managed by the enterprise or by the service provider.










No comments:
Post a Comment